You’ll dive with more technical precision after understanding this key principle.
Let me tell you a story, something that’s happened to all of us at some point, but we didn’t realize it fully: one of those days when everything seemed perfect… until I almost messed up!
It was a dive in calm waters, with amazing visibility, everything going smoothly. Suddenly, I noticed my buoyancy wasn’t right, something felt off. I fixed it right away, but during my ascent, I felt I wasn’t fully in control of my speed and got a bit scared.
Do you know what happened?
I hadn’t considered how pressure and volume of air behave underwater. That’s when I realized that diving isn’t just about going underwater – it’s about understanding how the water around you works.
So, what does this have to do with Boyle’s Law and scuba diving? A lot.
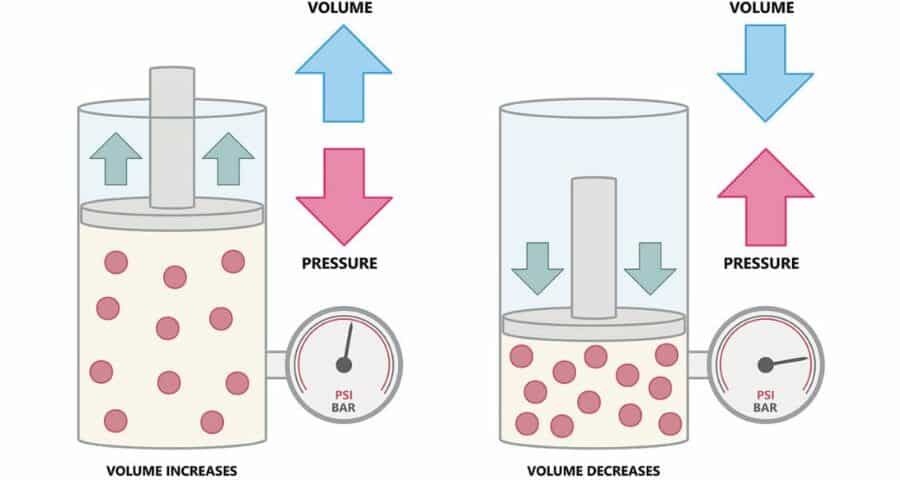
Boyle’s Law explains how pressure changes the volume of air, the air in your BCD, your wetsuit, and even your lungs. So, it’s key to controlling your buoyancy more precisely. I call it fine-tuned diving. And it helps with air consumption too.
Because if there’s one thing you learn over time, it’s that understanding the principles of physics isn’t just useful – it’s essential for advanced and efficient scuba diving.
Ever wondered:
- Why does your BCD inflate like a balloon when you ascend, even though you haven’t added air?
- Why does your air consumption spike when you go deeper?
- Or why do you ascend when you inhale, and descend when you exhale?
Well, my friend, you need to dive according to Boyle’s Law. Don’t worry, we won’t dive into crazy formulas (although, if you like that stuff, we’ve got you covered).
Boyle’s Law is just one of the gas laws in play when you’re underwater. These laws are like the commandments of scuba diving:
- Boyle: As pressure decreases, air expands. As pressure increases, air compresses. Simple, right?
- Charles, Henry, and the others: Each one has their own role, and all of them are equally important.
Want to learn how to control your buoyancy like a Jedi master? Avoid accidents and manage your air consumption? Keep reading to learn how to apply Boyle’s Law in scuba diving.